What is a Digital input Module?
Share
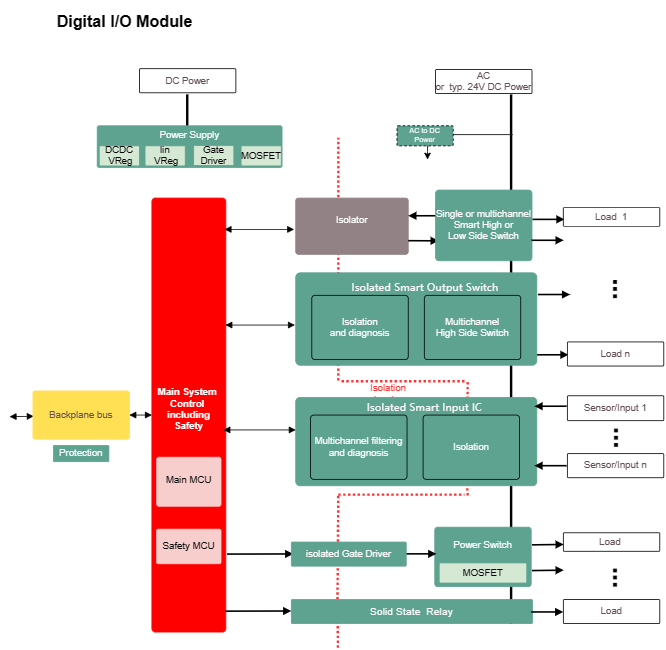
A digital input module, also known as a digital input card or digital input interface, is a component commonly used in automation and control systems. Its primary function is to interface with and monitor digital signals from external devices or sensors, converting these signals into data that can be processed by a controller or computer.

Key features and functions of a digital input module include:
-
Input Channels: A digital input module typically has multiple input channels, each capable of monitoring the state of a digital signal. These channels are used to connect external devices or sensors, such as switches, sensors, or other digital sensors.
-
Digital Signals: Digital input modules handle binary digital signals, which can be in one of two states: ON (typically represented as a logic high or '1') or OFF (represented as a logic low or '0'). They detect and report the state of these signals to the controller.
-
Isolation: Many digital input modules provide electrical isolation between the external devices and the internal electronics. Isolation helps protect the controller or computer from electrical noise, voltage spikes, and potential hazards that may occur in the external environment.
-
Signal Processing: The module processes the incoming digital signals and sends the information to the controller or computer for further processing. This can include tasks like monitoring the status of switches, detecting events, or capturing data from sensors.
-
Compatibility: Digital input modules are designed to work with specific control systems or controllers, such as Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) or data acquisition systems. They are often available in various configurations to match the requirements of the system they are integrated into.
-
Scalability: In industrial and automation applications, digital input modules are often scalable, allowing users to add more modules as needed to accommodate a larger number of input signals.
Common applications of digital input modules include monitoring the state of limit switches, push buttons, proximity sensors, and other devices in industrial automation, manufacturing, and control systems. They are essential for collecting data about the status of digital devices or events in real-time, enabling the control system to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions.
